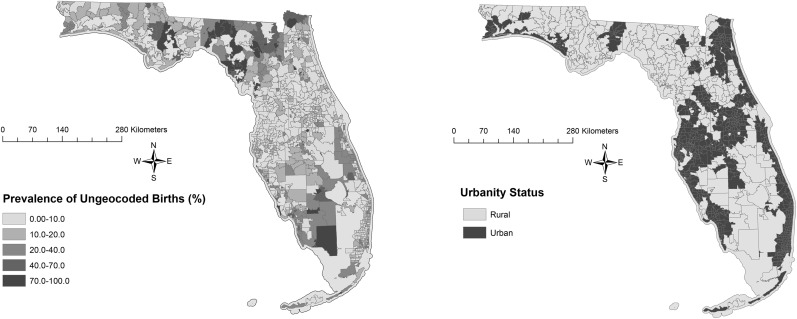
Fall Course: GEO3452 GEO6421 Medical Geography
This course provides a comprehensive survey of geographic topics and approaches in medical sciences, including: human ecology of diseases, research methods, geospatial techniques, landscape epidemiology, weather and climate, pollution issues, urban health, administration and planning, etc. What you will learn: -Basic concepts, principles, and methods that are widely used in medical geography studies; -A variety […]