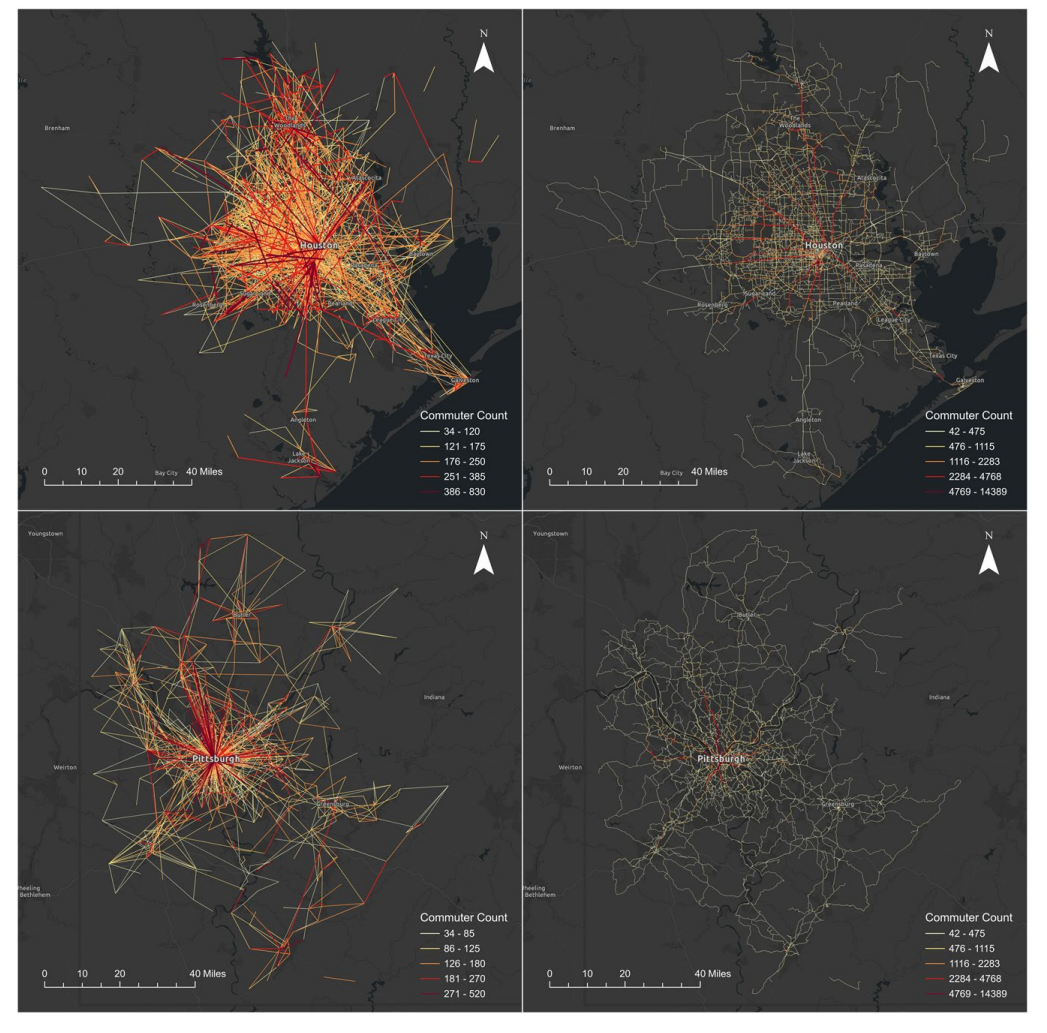
Commuting backbones represent the most essential connections within a commuting network—those significant flows that link major residential and employment areas and structurally support regional mobility systems.
Identifying these backbones is critical for understanding large-scale travel demand, informing infrastructure investment, and supporting transportation planning at regional and national levels. Despite their importance, no publicly available datasets currently exist that capture these commuting backbones across the United States.
This paper addresses this gap by generating and sharing two commuting backbone networks, focusing on ground-based commuting modes. Using the disparity filter algorithm, the study extracts significant commuter flows—forming the commuter connection backbone network—within core-based statistical areas (CBSAs).
These connections are then mapped to the road network to determine shortest driving paths, and aggregated to highlight heavily used road segments, resulting in the backbone road network.
These datasets offer a consistent, national framework for examining key commuting corridors, analyzing structural characteristics of commuting networks, and supporting applications in transportation planning, infrastructure prioritization, sustainability analysis, and regional policy development.
Wang, J., & Hu, Y. (2025). Constructing the commuting backbone network dataset for the United States. Scientific Data 12, 1267.