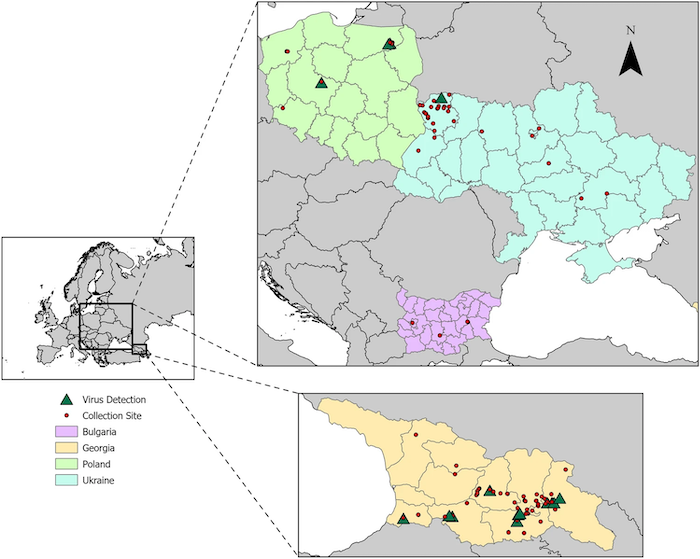
BLACKBURN – The expanding range of emerging tick-borne viruses in Eastern Europe and the Black Sea Region
Koray Ergunay, Brian P. Bourke, Drew D. Reinbold-Wasson, Mikeljon P. Nikolich, Suppaluck P. Nelson, Laura Caicedo-Quiroga, Nataliya Vaydayko, Giorgi Kirkitadze, Tamar Chunashvili, Lewis S. Long, Jason K. Blackburn, Nora G. Cleary, Cynthia L. Tucker & Yvonne-Marie Linton
Article first published online: 14 November 2023
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-46879-2
ABSTRACT: We analysed both pooled and individual tick samples collected from four countries in Eastern Europe and the Black Sea region, using metagenome-based nanopore sequencing (NS) and targeted amplification. Initially, 1337 ticks, belonging to 11 species, were screened in 217 pools. Viruses (21 taxa) and human pathogens were detected in 46.5% and 7.3%, respectively. Tick-borne viral pathogens comprised Tacheng Tick Virus 2 (TTV2, 5.9%), Jingmen Tick Virus (JMTV, 0.9%) and Tacheng Tick Virus 1 (TTV1, 0.4%). An association of tick species with individual virus taxa was observed, with the exception of TTV2, which was observed in both Dermacentor and Haemaphysalis species. Individual ticks from pools with pathogen detection were then further screened by targeted amplification and then NS, which provided extensive genome data and revealed probable pathogen Haseki Tick Virus (HTV, 10.2%). Two distinct TTV2 clades were observed in phylogenetic analysis, one of which included closely related Dermacentor reticulatus Uukuviruses. JMTV detection indicated integrated virus sequences. Overall, we observed an expansion of newly documented pathogenic tick-borne viruses into Europe, with TTV1 being identified on the continent for the first time. These viruses should be included in the diagnostic assessment of symptomatic cases associated with tick bites and vector surveillance efforts. NS is shown as a useful tool for monitoring tick-associated pathogens in pooled or individual samples.
Read the full publication in Scientific Reports.