ASH – Modes of climate mobility under sea-level rise
Nadia Seeteram, Kevin Ash, Brett Sanders, Jochen Schubert, Katharine Mach
Article first published online: 16 October 2023
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/acfe22
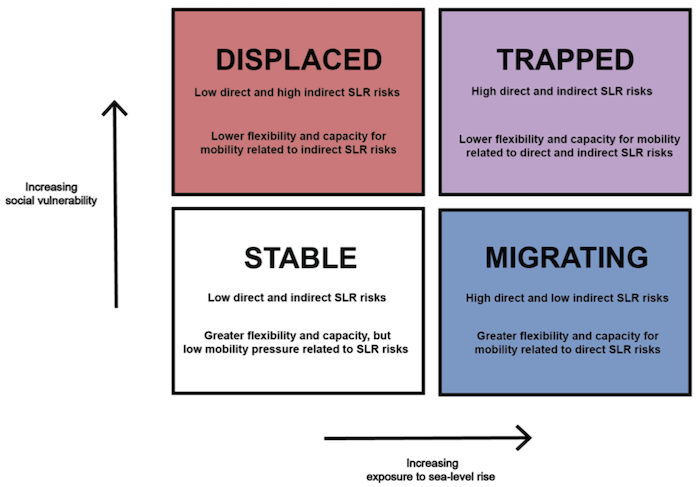
ABSTRACT: Exposure to sea-level rise (SLR) and flooding will make some areas uninhabitable, and the increased demand for housing in safer areas may cause displacement through economic pressures. Anticipating such direct and indirect impacts of SLR is important for equitable adaptation policies. Here we build upon recent advances in flood exposure modeling and social vulnerability assessment to demonstrate a framework for estimating the direct and indirect impacts of SLR on mobility. Using two spatially distributed indicators of vulnerability and exposure, four specific modes of climate mobility are characterized: (1) minimally exposed to SLR (Stable), (2) directly exposed to SLR with capacity to relocate (Migrating), (3) indirectly exposed to SLR through economic pressures (Displaced), and (4) directly exposed to SLR without capacity to relocate (Trapped). We explore these dynamics within Miami-Dade County, USA, a metropolitan region with substantial social inequality and SLR exposure. Social vulnerability is estimated by cluster analysis using 13 social indicators at the census tract scale. Exposure is estimated under increasing SLR using a 1.5 m resolution compound flood hazard model accounting for inundation from high tides and rising groundwater and flooding from extreme precipitation and storm surge. Social vulnerability and exposure are intersected at the scale of residential buildings where exposed population is estimated by dasymetric methods. Under 1 m SLR, 56% of residents in areas of low flood hazard may experience displacement, whereas 26% of the population risks being trapped (19%) in or migrating (7%) from areas of high flood hazard, and concerns of depopulation and fiscal stress increase within at least 9 municipalities where 50% or more of their total population is exposed to flooding. As SLR increases from 1 to 2 m, the dominant flood driver shifts from precipitation to inundation, with population exposed to inundation rising from 2.8% to 54.7%. Understanding shifting geographies of flood risks and the potential for different modes of climate mobility can enable adaptation planning across household-to-regional scales.
Read the full publication in Environmental Research Letters.