RYAN – Comparing prioritization strategies for delivering indoor residual spray (IRS) implementation, using a network approach
AUTHOR LIST
Article first published online: SEPT 2020 Malaria Journal
DOI: 10.1186/s12936-020-03398-z
Background
Indoor residual spraying (IRS) is an effective method to control malaria-transmitting Anopheles mosquitoes and often complements insecticide-treated mosquito nets, the predominant malaria vector control intervention. With insufficient funds to cover every household, malaria control programs must balance the malaria risk to a particular human community against the financial cost of spraying that community. This study creates a framework for modelling the distance to households for targeting IRS implementation, and applies it to potential risk prioritization strategies in four provinces (Luapula, Muchinga, Eastern, and Northern) in Zambia.
Methods
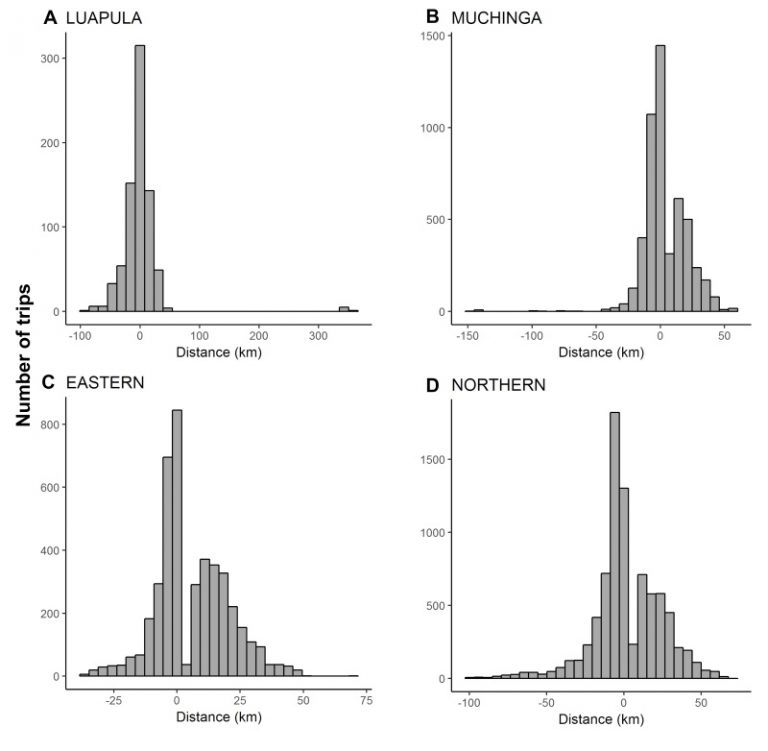
Optimal network models were used to assess the travel distance of routes between operations bases and human communities identified through remote sensing. Network travel distances were compared to Euclidean distances, to demonstrate the importance of accounting for road routes. The distance to reaching communities for different risk prioritization strategies were then compared assuming sufficient funds to spray 50% of households, using four underlying malarial risk maps: (a) predicted Plasmodium falciparum parasite rate in 2–10 years olds (PfPR), or (b) predicted probability of the presence of each of three main malaria transmitting anopheline vectors (Anopheles arabiensis, Anopheles funestus, Anopheles gambiae).
Results
The estimated one-way network route distance to reach communities to deliver IRS ranged from 0.05 to 115.69 km. Euclidean distance over and under-estimated these routes by − 101.21 to 41.79 km per trip, as compared to the network route method. There was little overlap between risk map prioritization strategies, both at a district-by-district scale, and across all four provinces. At both scales, agreement for inclusion or exclusion from IRS across all four prioritization strategies occurred in less than 10% of houses. The distances to reaching prioritized communities were either lower, or not statistically different from non-prioritized communities, at both scales of strategy.
Conclusion
Variation in distance to targeted communities differed depending on risk prioritization strategy used, and higher risk prioritization did not necessarily translate into greater distances in reaching a human community. These findings from Zambia suggest that areas with higher malaria burden may not necessarily be more remote than areas with lower malaria burden.
Read the full publication at Malaria Journal